What is a dishwasher?
 Many homemakers have never encountered a dishwasher, and only know of their existence through hearsay. While they have a basic understanding of the appliance—it washes dishes—only a small group of users possesses more in-depth knowledge. We'll attempt to describe how a dishwasher works, explore its functions and options, discuss the various designs, and understand how useful such a device can be.
Many homemakers have never encountered a dishwasher, and only know of their existence through hearsay. While they have a basic understanding of the appliance—it washes dishes—only a small group of users possesses more in-depth knowledge. We'll attempt to describe how a dishwasher works, explore its functions and options, discuss the various designs, and understand how useful such a device can be.
What is this device and how does it work?
A dishwasher is a complex electromechanical device designed to automatically clean dishes. The first primitive unit was invented back in the 19th century, and over the next two centuries, it has been constantly improved and modified. Dishwashers can be used in homes, for multiple customers, and in catering establishments. The machine consists of the following components:
- A washing chamber that includes a lower and upper basket, as well as a cutlery tray. Some models may be equipped with a separate glassware wash area;
- container for detergents;
- sprayer and nozzle systems;
- power supply wiring;
- A heating element responsible for heating cold water to a set temperature;
- control panels, including various buttons, switches and indicators;
- sealing door;
- drainage system;
- thermal insulation material;
- door locking devices;
- water intake valve;
- softening filter;
- a tank for a salt composition with an ion exchanger, etc.
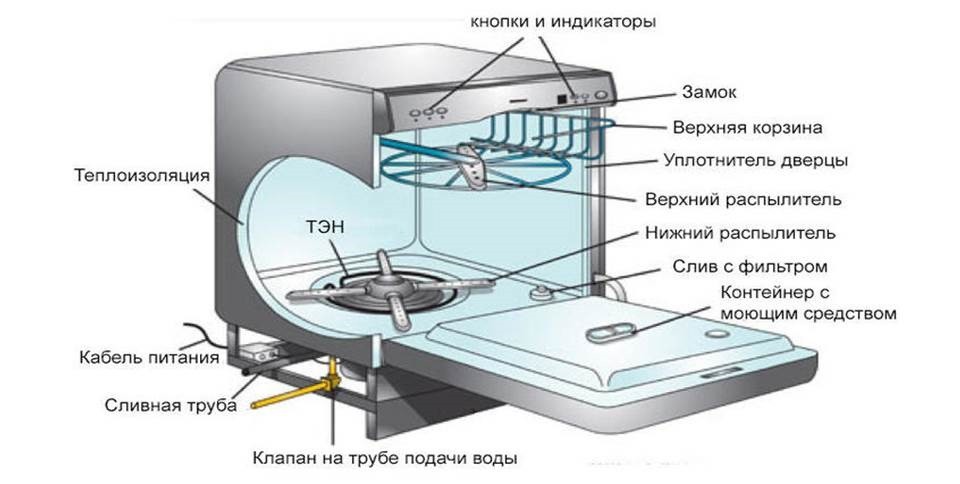 Depending on the user's cleaning mode, the dishwasher can fill with cold water from 1 to 5 times. Once in the system, the water is forced under pressure through a softening filter element, heated by a heating element, and then transferred to the spray arms located above the baskets. The speed of the water jets washing the cutlery, and therefore the cleaning time and the quality of the wash, directly depend on the power of the pump that supplies the water. Manufacturers rarely highlight this important parameter in the appliance's specifications; usually, only the overall power of the dishwasher is specified.
Depending on the user's cleaning mode, the dishwasher can fill with cold water from 1 to 5 times. Once in the system, the water is forced under pressure through a softening filter element, heated by a heating element, and then transferred to the spray arms located above the baskets. The speed of the water jets washing the cutlery, and therefore the cleaning time and the quality of the wash, directly depend on the power of the pump that supplies the water. Manufacturers rarely highlight this important parameter in the appliance's specifications; usually, only the overall power of the dishwasher is specified.
Sprayers rotate around their axis, spraying jets of water onto dishes placed in trays. The liquid flows into a tray located at the bottom of the chamber, then passes through a mesh filter element and into a special reservoir, from where it returns to the feed pump. Once the primary cleaning cycle is complete, the wastewater is discharged into the sewer through a drain pipe.
During the wash cycle, the appliance automatically dilutes the detergent added by the user. The cutlery is then rinsed. Some dishwasher models are also equipped with a water purity sensor, which allows you to check the quality of the water after rinsing.
Main parameters
Now that we've covered what a dishwasher is and how it works, let's move on to another important question: "What parameters and characteristics of the model should you pay attention to when choosing?"
First, you should definitely consider the dishwasher's size. Many housewives hesitate to buy a dishwasher precisely because of insufficient kitchen space. However, today you can find fairly compact appliances that can be integrated into cabinetry. The dishwasher's size directly affects its capacity:
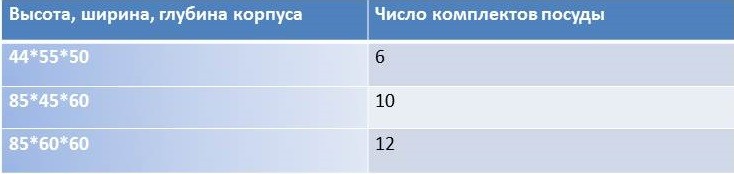
Manufacturers define one set of tableware as 4 plates, a mug, a fork and a spoon.
A 10-place setting wash chamber can accommodate a few extra plates, as there are no standardized sizes. Therefore, it's important to understand that the stated capacity is only an approximate value.
It's important to remember that placing pots, pans, or baking sheets in the basket will take up space that would be enough to wash 4-5 place settings. Machines with a stated capacity of up to six place settings are suitable for families of one or two people, while average families are better off purchasing machines with a minimum capacity of 10 place settings.
Let's look at other technical characteristics of the dishwasher that you need to pay attention to.
- Water consumption. This equipment uses significantly less water per cleaning cycle than a manual wash. On average, manufacturers claim roughly the same volume, 10-14 liters. Consumption can be adjusted by the user by selecting energy-saving programs or using the "half load" option.
- Energy consumption. The electricity consumed by the machine during operation is an important parameter. It's best to choose equipment with the highest energy efficiency rating. This will significantly reduce the cost of a single wash due to the lower kilowatt consumption.
- Power. Powerful machines will clean much more efficiently and quickly. A shorter standard wash cycle will reduce energy consumption.
- Noise level. A classic operational parameter indicating the volume of a dishwasher's operation. For a one-room apartment or studio, it's best to choose a dishwasher with a low decibel level (up to 45 dB), as the dishwasher is almost always run at night. If the kitchen is located far from the bedroom, it's acceptable to purchase a noisier model.
- Washing class. The higher the class, the more effectively all stains on dishes will be removed.
- Drying class. "A, A+, A++" categories assume that utensils will be removed from the chamber completely dry, while "C" class allows for some water droplets to remain on the surface of the dishes.
I'd like to discuss the drying type in more detail. It determines the conditions under which cutlery will dry. There are condensation, convection, and turbo drying.
Condensation involves the natural evaporation of water from the surface. After rinsing, dishes are doused with hot water, and any water droplets remaining on the cutlery evaporate, settling on the cool walls of the chamber. The main advantage of this type of drying is its simplicity—no additional equipment or parts are required to ensure drying. Consequently, condensation drying machines are slightly less expensive.
The disadvantage of the condensation method is the lengthy drying process and less-than-perfect drying results. Drops, streaks, and small puddles of water often remain on dishes. Excessive residual moisture in the dishwasher's compartment can cause an unpleasant odor, so be sure to leave the dishwasher door open for ventilation after drying.
Convective drying involves drying dishes by creating air exchange in the chamber. A heat exchanger accelerates drying by convective air movement. In some devices, convective drying is achieved through ventilation holes in the appliance body.
Dishwashers with this type of drying system cost a little more, but they provide the most effective drying of washed items.
A turbo dryer operates using a heater and a fan. The heating element warms the air in the chamber, and the fan circulates it within the machine. This allows moisture to evaporate much faster. This type of drying is the most effective, but also the most expensive: firstly, these models are more expensive, and secondly, they consume more energy.
Almost all dishwashers from any manufacturer are equipped with an ion-exchange filter. It's essential to soften hard water entering the system. Excessively hard water can cause the heating element to fail. Water passing through the ion exchanger is saturated with salt ions, and magnesium and calcium particles remain in the tank, so the liquid becomes much softer.
Over time, the filler loses its properties and must be regenerated with a salt solution.
The dishwasher's ion exchanger has a special salt container. It must always contain sodium chloride at a preset level. Some models are equipped with a special indicator that monitors the salt level in the container.
Sodium chloride consumption is manually set by the user, depending on the water hardness in your region. Once you know the level, you can adjust the salt consumption regulator according to the user manual. New dishwashers have an option to automatically detect tap water hardness. This will automatically regulate sodium chloride consumption.
Description of common washing modes
All dishwasher models have not one, but several cleaning functions. The user can independently select one or another program depending on the level of contamination of the dishes. Let's look at the definitions of the most common washing modes.
- Express Clean. Helps quickly clean lightly soiled cutlery. The program duration is significantly shorter than the standard cycle.
- The economy mode allows you to save water and electricity resources to the maximum extent possible.
- Intensive wash. This program heats the water to the highest possible temperature. This program will consume more energy. The benefits of intensive cleaning are significant – dishes are virtually sterilized, meaning they are completely free of bacteria. When using the intensive program, it's best to avoid placing plastic or thin glass items in the dishwasher, as these materials can be damaged by the high temperature.
- Delicate cycle. Ideal for cleaning delicate dishes. The heating element heats the water to 45°C, making this cycle suitable for all types of items.
- Rinsing. This involves quickly washing dishes without the use of household chemicals. It's typically used to refresh clean dishes that have been sitting in the cupboard for a long time.
- Pre-soaking. This option is considered one of the most important. A dishwasher can effectively remove only fresh stains. Often, housewives "build up" the dishes until they're full, resulting in food residue drying and sticking firmly to the surface of kitchen appliances. The same applies to burnt-on food. So, before cleaning, it's essential to soak the dishes. This can be done in the sink, but it's much more convenient to have the dishwasher do this.
- Half Load. An economical program that runs when only one basket in the machine chamber is full. This reduces water and detergent consumption by half. However, the efficiency of this cycle will be lower than with a standard cleaning cycle.
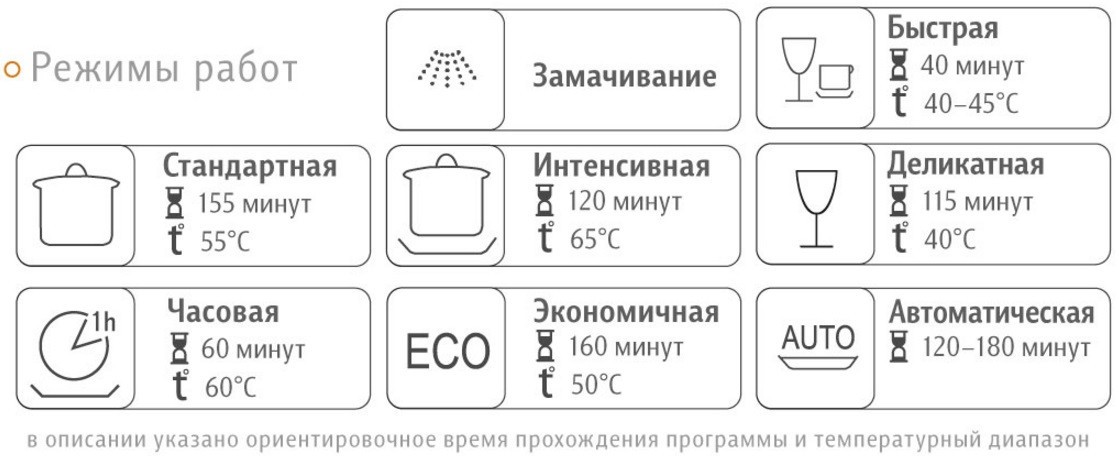
By purchasing a dishwasher with a sufficiently wide range of functions, you can customize its operation to suit each specific wash. This means you'll have the ability to independently control the wash time and, consequently, the consumption of all types of resources.
The principle of selection of equipment
Every family should choose the optimal dishwasher capacity based on their needs. If you enjoy entertaining, or your family advocates a healthy five-meal-a-day diet, a significant amount of dirty dishes will accumulate by the evening, requiring a larger dishwasher even for three people. Conversely, if your family is busy with work, school, and other activities until the evening and only gathers for dinner, you might want to consider a compact appliance.
On average, a dishwasher for 10-13 sets of dishes will be enough for a family of 4.5 people.
Also, focus on your specific preferences: if speed of washing is important to you, choose units with turbo drying and increased power. When the primary parameter is the cleanliness of the dishes being washed, look at the washing class of the equipment. The soaking function will be necessary for housewives who do not want to accumulate soaking dishes in the sink.
Interesting:
Readers' comments
Headings
Washing machine repair


For buyers
For users

Dishwasher

















Add a comment