Washing machine motor specifications
 It often happens that a component in an automatic washing machine completely fails, making repairs impractical. However, it contains many parts that can be useful around the home. For example, electric motors are often used by DIYers to build various machines. First, you need to understand the technical specifications of a washing machine motor to determine what kind of device you have and what kind of DIY project you can create with it.
It often happens that a component in an automatic washing machine completely fails, making repairs impractical. However, it contains many parts that can be useful around the home. For example, electric motors are often used by DIYers to build various machines. First, you need to understand the technical specifications of a washing machine motor to determine what kind of device you have and what kind of DIY project you can create with it.
Types of washing machine motors
The washing machine's electric motor is a reliable part that very rarely breaks down. That's why Motors from cars that have been in use for 20-30 years are quite suitable for recycling. With their help, craftsmen construct lathes and grinding machines, apple and grain crushers, small concrete mixers, lawn mowers, and other useful household devices.
Washing machines can be equipped with a collector, inverter or asynchronous electric motor.
Let's explore the differences between electric motors and the characteristics specific to each power device. We'll also explain the components that make up different motors.
Brushed motors are considered the most common today, found in most automatic washing machines. The design of such an electric motor includes:
- aluminum body;
- rotor;
- stator;
- two brushes;
- tachometer.
These motors can have between 4 and 8 terminals. Electric brushes are required to establish a connection between the rotor winding and the motor. The commutators are installed at the bottom of the washing machine. The motor pulses are transmitted to the drum pulley via a belt drive.
Inverter motors are considered the most modern. They first appeared in washing machines from the South Korean brand LG in 2005. Today, this innovative development is used by many manufacturers—direct-drive washing machines are produced by brands such as Bosch, Samsung, Haier, Whirlpool, AEG, and others.
Inverter motors are connected directly to the drum. These machines eliminate the need for a pulley or drive belt. This type of motor design includes:
- rotor (it is a cover with magnets);
- stator (this is several clips with coils);
- frequency converter.
Inverters have no brushes, which must be replaced every 3-5 years on the commutators. The armature is formed by magnets. During operation, voltage is directed to the stator winding, converting it into inverter voltage.
Asynchronous motors are rarely used in automatic washing machines these days, but they are still found in older activator washing machines. These motors come in two- and three-phase versions. These motors can be found in early Bosch, Candy, and Ardo models.
The asynchronous motor in washing machines is located underneath and is connected to the drum via a drive belt. The design consists of a rotor and a stationary stator. These motors are simple and low-maintenance. If the bearings are replaced regularly, the machines can operate for decades without any problems.
Characteristics of asynchronous electric motors
Asynchronous motors can be found in the earliest models of actuator washing machines from brands like Bosch, Candy, Miele, and Ardo. These are the most primitive electric motors with the simplest design. These motors can operate in ambient temperatures ranging from -60 to +85°C.
In terms of design, an asynchronous motor consists of two main parts: a rotor and a stator.
The stator of an electric motor is a stationary element consisting of a metal housing and a winding. The rotor is a rotating component containing a core and a shaft. The core is made of several steel laminations and serves as the base for the rotor winding.
The scope of application of such engines is quite wide. Using an asynchronous motor from an old car, you can make a lathe or grinding machine, a pump station, a lawn mower, a fan, a gearbox, and other systems. This is why DIYers never throw away the electric motor from a broken washing machine, but give it a “second life.”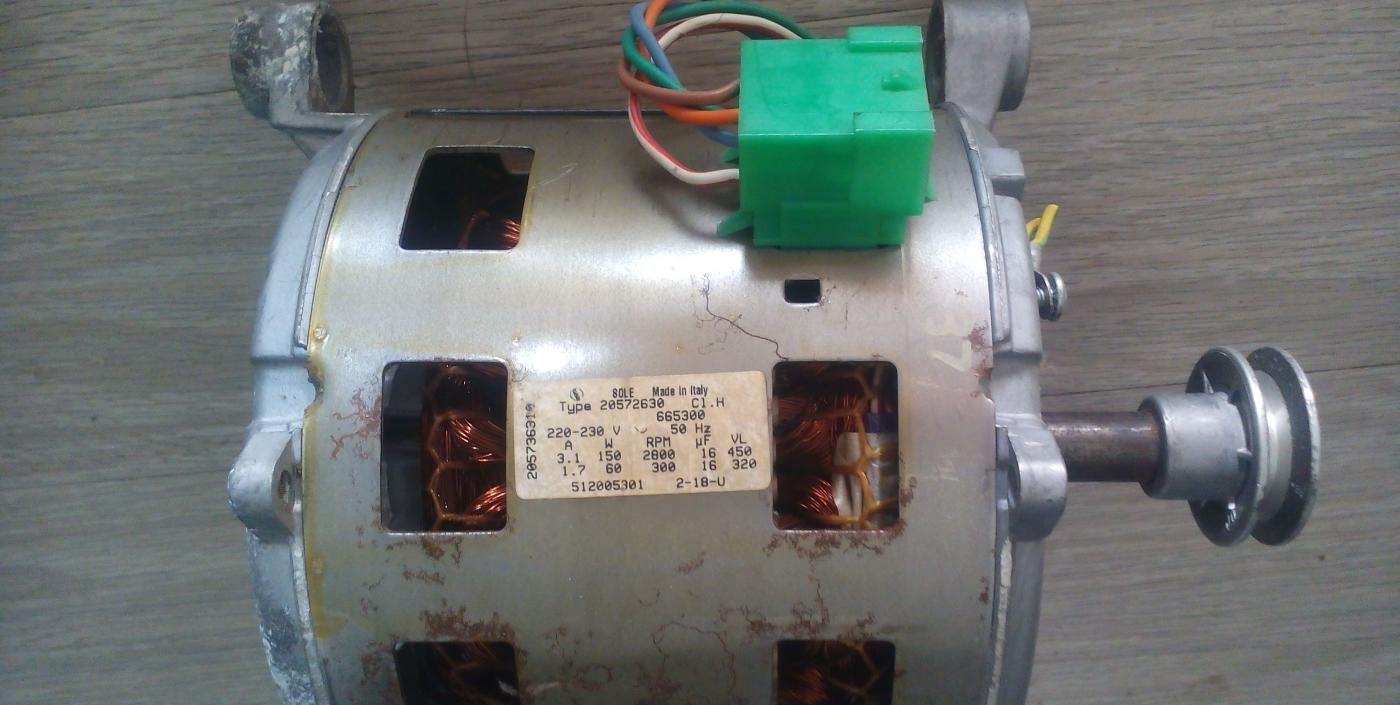
The general technical characteristics of asynchronous power devices found in actuator washing machines are as follows:
- power – from 180 to 360 watts;
- received voltage – 220 Volts (+-22 V);
- synchronous rotation speed – up to 3000 rpm.
During operation, an asynchronous motor produces noise levels of approximately 50 dBA. Some models of power devices may have built-in thermal protection. Manufacturers typically set the following operating limits for such electric motors:
- up to 30 starts per hour;
- no more than two hundred launches in 24 hours;
- The total number of launches per year is no more than 30 thousand.
At operating temperature, these motors can withstand a 20% increase in speed for 120 seconds without any deformation or other damage. They can also withstand a 50% overcurrent for 2 minutes. All this demonstrates the high reliability of this type of power device.
Characteristics of brushed electric motors
These motors replaced asynchronous motors and held their position for a long time. Today, approximately 80% of low- and mid-price washing machines are equipped with these motors. The operation of collectors can be provided by either direct or alternating current.
As mentioned earlier, the commutator consists of a stator, a tachometer that regulates rotation speed, a rotor, bearing shields, and at least two brushes. The graphite rods tend to wear down, so they need to be replaced periodically.
The advantages of these collectors include compact dimensions, high starting torque, and high speed. A simple control circuit is also a plus.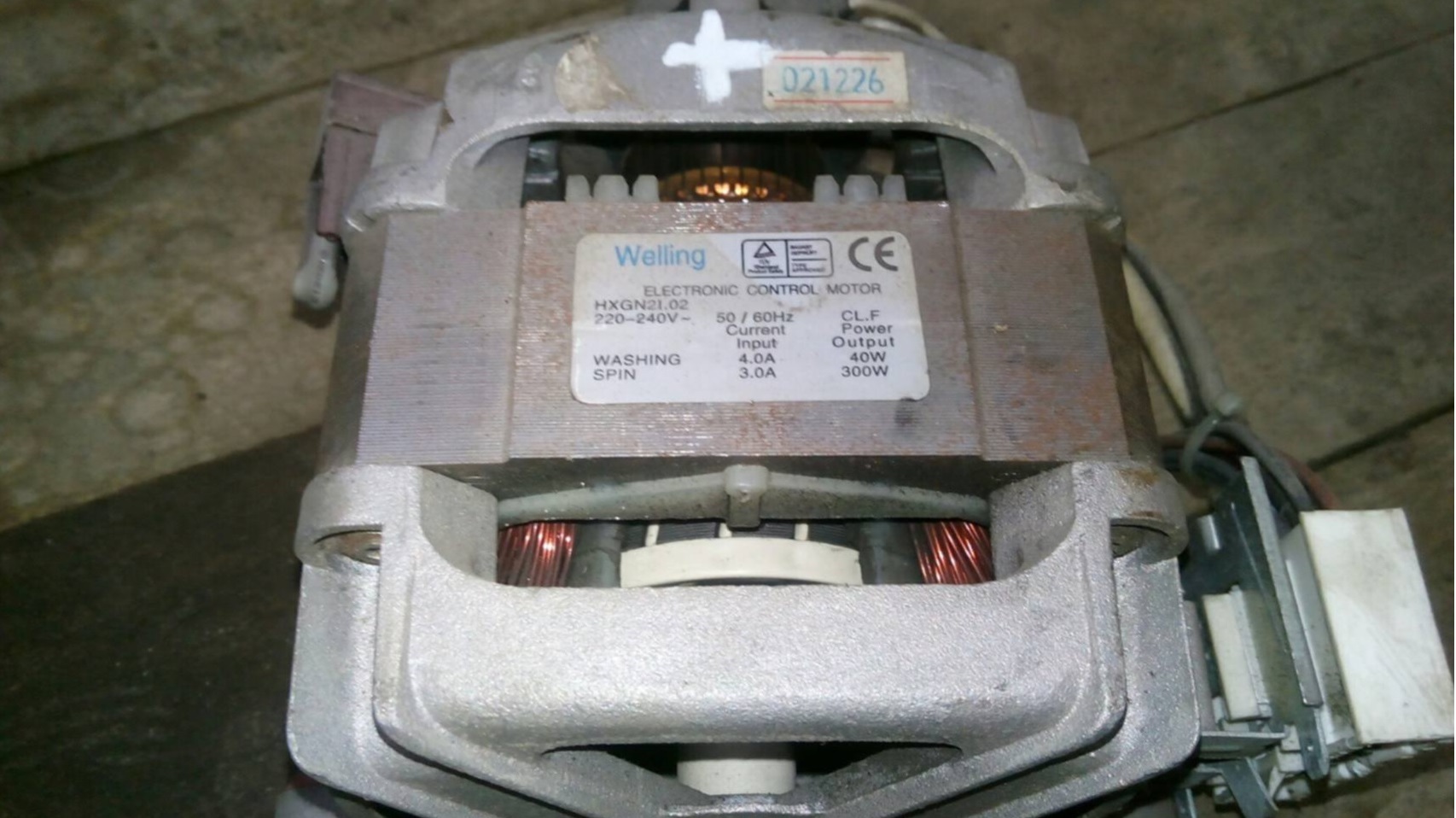
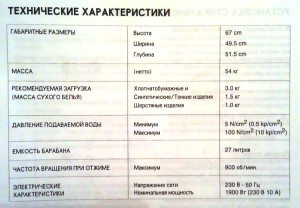
The technical characteristics of this type of engine can be understood using the DK76-280-12 manifold as an example. The key indicators are as follows:
- rated operating voltage – 210-230 Volts;
- frequency – 50 Hz;
- power – 0.5 kW;
- current consumption – 2.25-2.75 Amperes;
- Efficiency – not less than 55%.
The average service life of collector electric motors without repair is 5 years.
The DK76-280-12 commutator rotor is a 12-slot assembly made of durable electrical steel, mounted on a shaft. The slots contain a double-layer winding. A fan is located on the armature shaft, supplying cooled air. This motor is supported by plain bearings, which are mounted in special bearing housings.
The connection between the rotor, stator, and outer winding is ensured by electric brushes located in special side holders. The brushes wear during operation, requiring periodic replacement. Another drawback of commutators is increased noise.
Typically, the power of commutator motors installed in automatic washing machines ranges from 380 to 800 watts. Therefore, before reusing a dismantled power device, it's best to check the markings on the housing and study the specific model's specifications in more detail.
Before connecting the motor outside the washing machine, figure out which terminal on the collector is used for what purpose. A couple of contacts are needed to connect the tachogenerator, so they most likely won't be needed. The remaining terminals are used as shown in the diagram.
Characteristics of inverter electric motors
Around the 2000s, with the development of semiconductor devices, frequency converters began to be widely used. These devices can change frequency and adjust voltage over a wide range, ranging from 1 to 500 Hz.
An inverter motor is not powered directly by the power grid, but by a built-in converter. The device automatically adjusts to the operating mode and produces the optimal voltage level and frequency. Therefore, an inverter is actually two devices combined in a single housing.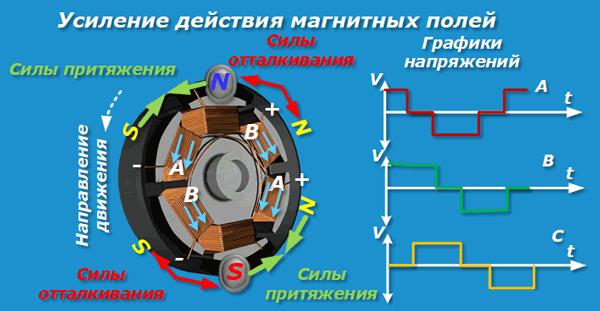
Using inverter technology allows for a wide speed range and multi-level operation of the electric motor. The built-in converter allows for voltage adjustment, resulting in optimal torque. Of course, all this is possible within certain limits, but the overall performance of these motors is significantly improved.
Due to their more complex design, the price of inverter motors is higher than that of collector and asynchronous motors.
The inverter converter corrects the voltage in two stages:
- accepts mains voltage and converts it into direct current;
- Creates a flow of positive and negative pulses from a constant voltage. This produces the required frequency, which is fed directly to the motor.
Some inverters have an additional conversion stage. At the final stage, the pulses are "added" to form a sine wave. However, the shape of the supplied voltage has little effect on the motor's operation, so many motors do not include this process.
The technical features of inverter motors allow for wide control of their operation. The motor can independently regulate its speed, convert voltage, and so on.
Interesting:
Readers' comments
Headings
Washing machine repair


For buyers
For users

Dishwasher
















Add a comment