How does an inverter motor work in a washing machine?
 Many modern automatic washing machines are equipped with inverter motors. Thanks to advertising, users know that these brushless motors are much more reliable than brushed motors. We'll explain the advantages of these devices and examine their operating principles.
Many modern automatic washing machines are equipped with inverter motors. Thanks to advertising, users know that these brushless motors are much more reliable than brushed motors. We'll explain the advantages of these devices and examine their operating principles.
What is the essence of "inverter technology"?
Many buyers are willing to pay a premium for an inverter motor in their washing machine. And this is entirely reasonable – these motors are more reliable than their brushed counterparts and, unlike their brushed counterparts, don't require periodic maintenance. In addition, machines with direct drive wash almost silently, which makes the machine more convenient to use.
A washing machine cannot function without an electric motor. For the machine to wash in different modes, it requires a motor with variable speeds. Motor speed is regulated in two ways: by changing the frequency or voltage.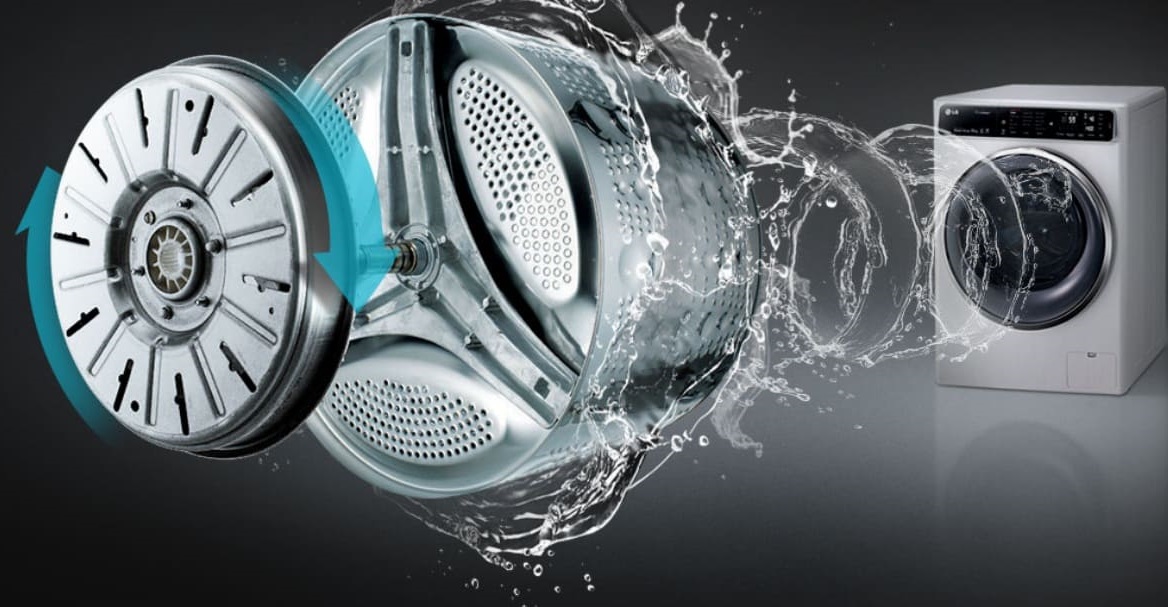
Before the invention of inverters, engine speed was adjusted directly by changing the voltage, and only within small limits. In this case, smooth, seamless speed changes were impossible. Only commutators could handle this, but even they had low torque under intensive operation, limiting their usefulness.
Literally in the 1990s and 2000s, with the development of semiconductors, frequency converters began to be used increasingly in production. They made it possible to vary motor frequency over wide ranges, from a minimum of 500 Hz to 500 Hz.
An inverter motor does not take current directly from the electrical network, but through a frequency converter built into it.
An inverter motor in a washing machine combines two components: a motor and a frequency converter. Based on the selected operating mode, the motor generates the required voltage and sets the desired speed. This technology was immediately adopted by washing machine manufacturers.
An inverter can quickly adjust voltage, ensuring optimal torque. This technology allows the desired RPM to be quickly reached and maintained. The overall technical characteristics of this type of motor are much better, but they are also more expensive.
How does an inverter converter work?
It's worthwhile to explain the operating principle of inverter motors. In fact, understanding this information doesn't require any special knowledge. The inverter built into the motor changes the voltage in two stages:
- receives voltage from the network, “rectifying” it;
- creates opposite-pole pulses from constant voltage.
The second stage produces the required frequency, which is then transmitted to the motor. Some inverters have an additional conversion stage, where the charges are converted into a sine wave. However, the voltage supply form has virtually no effect on the operation of the electric motor, so this unit is not included in washing machines.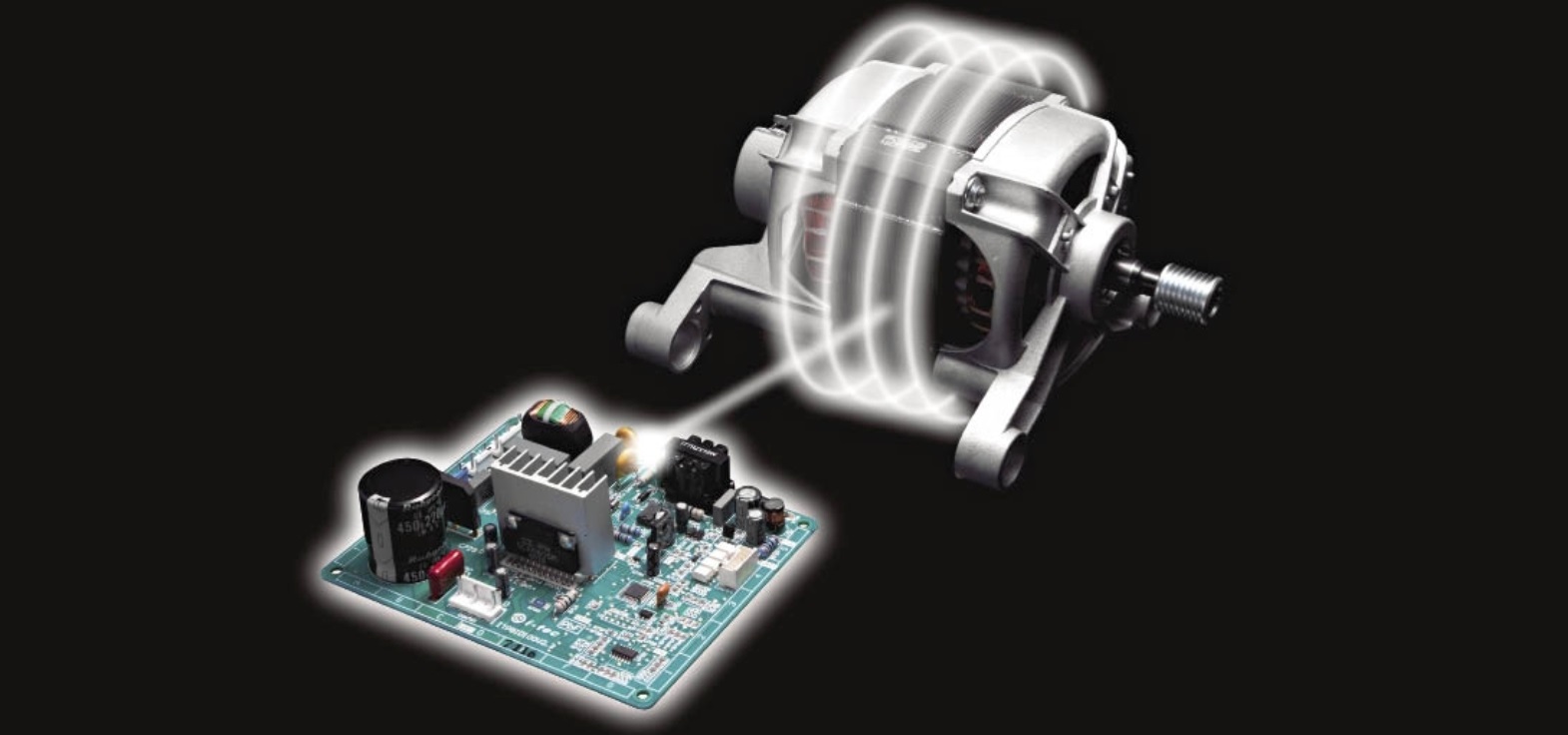
All processes in modern automatic washing machines are controlled by a main electronic module. It determines the required voltage, thereby controlling the motor speed. The number of revolutions will vary depending on the washing algorithm and the stage of the cycle (minimum during soaking, maximum during spinning).
Features of using motors in washing machines
Today, washing machines with both brushed and inverter motors are available on the market. Budget-friendly machines typically use brushed motors. These motors can reach speeds of up to 10,000 rpm and produce a decent amount of torque. However, they also have some drawbacks: they are excessively noisy and require periodic brush replacement.
Inverter automatic machines are distinguished by a low noise level during operation.
Inverter motors have no brushes. These washing machines also have no belt drive, resulting in virtually silent operation. The new generation of motors uses a special monolithic rotor, which allows the motor itself to be made more compact.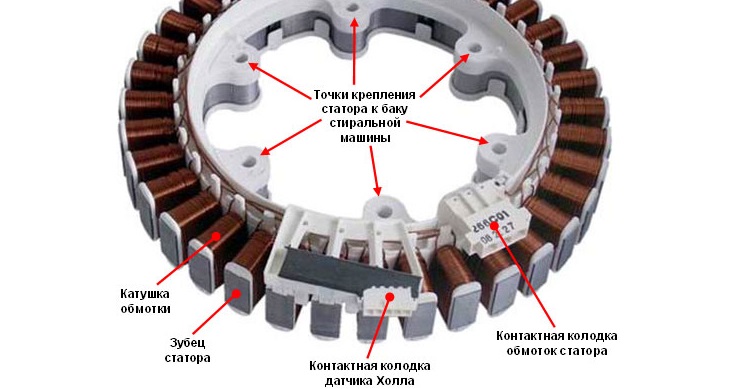
An inverter motor in a washing machine comes at a premium. A separate module is required to control it, often costing up to a quarter of the total machine price. Compared to brushed motors, inverters are considered more reliable. With the former, the user will have to replace the motor brushes every two to three years. The drive belt, which tends to stretch, can also cause problems.
Inverters don't have brushes, so they don't require periodic maintenance. Manufacturers also provide a ten-year warranty on inverter motors. Consequently, these motors rarely break down. They typically operate reliably well beyond their stated lifespan.
Interesting:
1 reader comment
Headings
Washing machine repair


For buyers
For users

Dishwasher

















I have a direct drive machine and I don’t regret it at all.