What is the voltage at the water inlet valve in a washing machine?
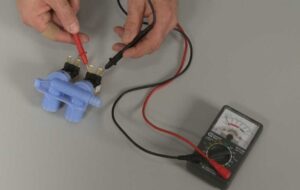 To test the solenoid valve of an automatic washing machine, you need to know the voltage supplied to it. When working with this element, it's important to follow safety precautions to avoid any accidents. Let's take a look at its basic characteristics.
To test the solenoid valve of an automatic washing machine, you need to know the voltage supplied to it. When working with this element, it's important to follow safety precautions to avoid any accidents. Let's take a look at its basic characteristics.
Main characteristics of the valve
Why is it important to understand the voltage supplied to the automatic transmission valve? This is necessary to assess potential risks and take all necessary precautions. Only after obtaining as much information as possible can diagnostics begin.
Many users are surprised when the inlet valve begins to hum after the cycle starts. This is due to the operating principle of the element. A spring is activated, the membrane opens, and water begins to flow into the system. Given the high pressure in the pipes, this sound is quite normal for the device to operate. The general characteristics of an inlet solenoid valve are as follows:
- received voltage – 220 volts;
- alternating current frequency – 50 Hz;
- thread size for connecting the inlet hose – 3/4;
- normal working pressure – up to 1 megapascal;
- nominal throughput capacity – 10 liters of water per minute at a pressure in the pipes of 0.3 megapascals;
- power – 8 watts;
- Nominal resistance: 3600 Ohm. Allowable deviation: ±5%.
If a washing machine's inlet valve breaks or becomes clogged, water stops flowing into the drum, preventing the machine from starting a wash. In this situation, you'll either need to replace the element or completely disassemble and clean it. Let's take a look at the components.
Intake valve design and materials
The element can be found under the top cover of the washing machine, in the area where the filler corrugated pipe is connected. The inlet valve is small in size and consists of a housing, a coil, a spring, a membrane and a core that blocks the water flow. The valve body is usually made of a temperature-resistant polymer. Steel or brass components are less common. An electromagnetic coil is attached to the "cartridge."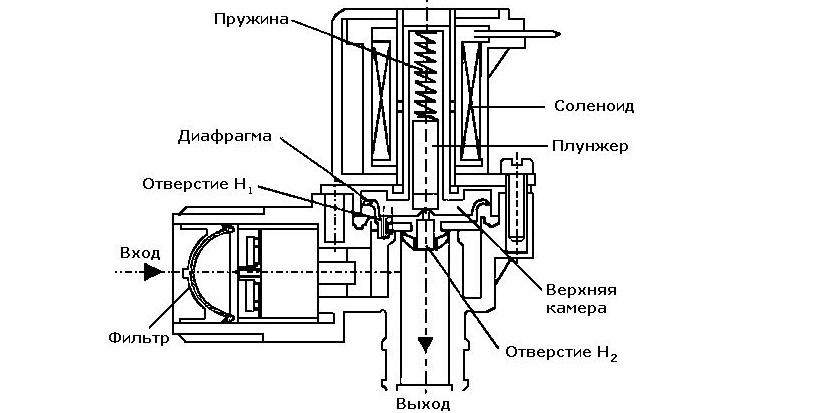
The coil contains magnets. The number of solenoids can vary from one to three. The number of coils depends on the number of valve sections. Different washing machines have single, double, triple, or quadruple units. The valve membrane is usually made of heat-resistant rubber. Less commonly, a rubber compound or silicone is used. The spring is self-explanatory; it's made of metal.
Inlet valves may differ in the number of sections, coils, and materials used, but the operating principle of the device remains the same.
How does this device work?
The washing machine's coils are controlled by the main control module. When static, and no voltage is applied to the valve, the membrane seals the machine, preventing water from entering. The design is so robust that it can withstand high water pressure.
When the user starts the washing machine, the control board sends a signal to the coil. The rod, sensing the electromagnetic pulses, is drawn into the coil, pulling the piston along with it. This opens the device, and water begins to flow into the drum. When the current is cut off, the membrane is pressed back against the housing seat, ensuring a completely sealed system.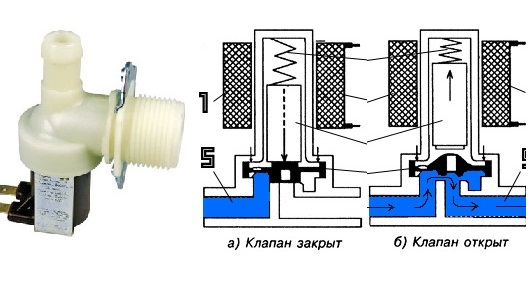
Washing machines manufactured 10-15 years ago are typically equipped with single-coil valves. In these models, water flow into the different compartments of the detergent drawer is controlled by a mechanical control unit. More modern models feature double and triple valves, with each coil responsible for its own compartment.
Typically, a detergent drawer has three sections. When such a machine has a dual-coil valve, water begins to flow into the third section when both solenoids are activated simultaneously. A pressure switch monitors the water level in the tank. Once the washing machine reaches the desired level, a sensor notifies the electronic module. The "brain" stops supplying voltage to the valve coils. This process repeats several times during the washing machine's cycle.
What breaks in the valve and how to replace it?
If your automatic washing machine refuses to fill with water or fills too slowly, you will have to inspect the solenoid valve and test it with a multimeter. Before performing diagnostics, be sure to de-energize the washing machine and turn off the shut-off valve. After this, you can detach the inlet hose from the rear wall of the housing.
The inlet valve mesh often gets clogged; to clean it, it is not necessary to disassemble the device.
To remove the filter, you'll need pliers. Detach the inlet hose from the machine and look closely – you'll see a metal mesh where it connects to the body. Grasp the protruding edges to remove the filter element. After cleaning, replace it.
If the washing machine was stored in a cool room, the water remaining in the valve may have frozen, causing the unit's housing to crack. In this case, the only solution is a complete replacement of the part. Sometimes, the solenoid coils fail. If one burns out and stops pulling the stem in, the valve will malfunction. The inlet element will need to be replaced. The procedure is as follows:
- de-energize the washing machine;
- turn off the water supply and detach the inlet hose from the body;
- remove the top panel of the case (or the side panel, for vertical models);
- Disconnect the wiring and pipes from the valve that connect it to the dispenser;
- Unscrew the bolts that secure the device to the housing;
- remove the old valve and install the serviceable one in its place.
To avoid any questions, it's a good idea to take a photo of the wiring diagram before disconnecting the wires. This will help avoid mistakes during reassembly. The replacement procedure is quite simple, and even a novice can handle it.
Interesting:
Readers' comments
Headings
Washing machine repair


For buyers
For users

Dishwasher
















Add a comment