Types of clothes dryers
 Everything that can be said about the classification of washing machines has already been said, but technology never stands still, and new helpers—tumble dryers—are increasingly becoming part of households. As with any appliance, before purchasing, you need to learn about the different types of clothes dryers available, how they differ, and which one is best for your specific needs. Let's find all the information you need and break it down.
Everything that can be said about the classification of washing machines has already been said, but technology never stands still, and new helpers—tumble dryers—are increasingly becoming part of households. As with any appliance, before purchasing, you need to learn about the different types of clothes dryers available, how they differ, and which one is best for your specific needs. Let's find all the information you need and break it down.
The main types of "dryers"
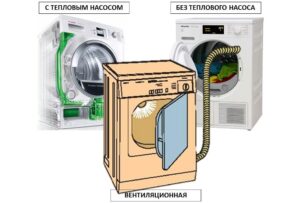
Dryers are primarily classified by drying type. Dryers can be ventilated or condensed. The difference lies in how the dryer removes moist air from the chamber. A ventilation device is less sophisticated in this regard: moist air is discharged through a special pipe directly to the street or into the ventilation system, so such a machine cannot be placed in a closed room without additional air drying devices.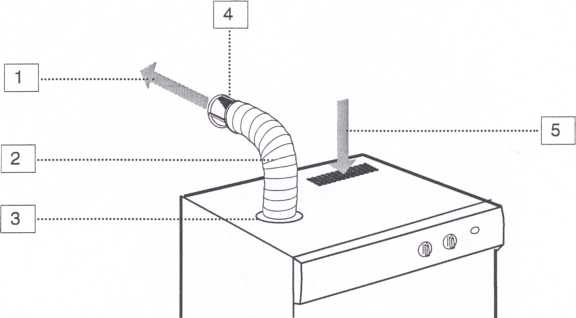
A condensation dryer extracts moist air into a special chamber, where the condensate is separated and collected in a reservoir. After the drying cycle, the reservoir must be emptied manually or the dryer can be connected to a drain. A condensation dryer can be installed anywhere.
Please note: If you plan to connect the condensation dryer to the sewer system, this will impose certain restrictions on its location (it must be close to utilities).
In terms of price, ventilation machines are significantly cheaper, but they consume much more electricity when operating.
Dryer equipped with a heat pump
Manufacturers of new-generation dryers have gone even further and equipped their units with a heat pump—a small refrigeration device built into the dryer that cools the air coming out of the drum containing the laundry.
In traditional dryers, air cooling occurs naturally due to the difference in temperature between the inside and outside. However, this mechanism has been deemed inefficient. Although logic dictates that an additional air-cooling device would consume more electricity, studies show that these dryers consume significantly less electricity than conventional dryers.
In addition, heat pumps serve a dual purpose. Not only do they capture heat as the air cools, but they also use it to heat the next batch of air entering the dryer drum. Thus, the energy consumed is used twice for the dryer, which is not only a clever and elegant engineering solution but also a convenient bonus for the average consumer. So, the extra cost for this type of dryer can be well worth it in everyday use.
What type of dryer is best to buy?
When choosing between these three types of dryers, don't settle on ventilation units. They're very picky when it comes to room selection, and using them in winter, when condensation doubles, is practically impossible. Choosing between condensation units and pump dryers is difficult. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, but they're quite similar in appearance and basic specifications.
- Load capacity. Both series offer units with varying load capacities, but in general, both types can dry 7-9 kg of laundry with a drum capacity of 80-120 liters.
- Both machines are very easy to operate: all processes are controlled by keys or touchscreen, and most models are equipped with a display.
- The program ranges of condenser and heat pump dryers also don't differ significantly: both have at least 10 standard modes. Some additional features and functions may be found across both product lines. The sensor set is generally similar across all dryers, including humidity and temperature monitoring and a condenser container fullness indicator. Some units also feature a filter clogging indicator.
- There are no significant differences in installation between different types of dryers. The key for both types is a nearby power outlet. If you want to connect a condensation dryer to a drain, position it accordingly. Heat pump dryers can exhaust moisture into the ventilation system, so the vent should be nearby. As for the room and the proximity of the dryer to the washing machine, for example, the choice is entirely up to the user. You can place the unit in a hallway, a closet, on a balcony, in a bathroom, in the kitchen, or next to, on top of, or above the washing machine.
- The only significant difference between these two types of dryers is that heat pump dryers are gentler on laundry, as the air temperature isn't very high. Heat pump dryers also consume less electricity, which is important for many. The advantage of condenser dryers is their significantly faster drying speed.
Important! Ultimately, for those who need to dry large loads of laundry regularly and in the shortest amount of time, condenser dryers are a better choice, especially since they're less expensive and less harmful.
Those who don't want to overpay while using a dryer, and those whose wardrobe consists primarily of delicate fabrics, should consider dryers with a heat pump.
As mentioned above, dryers without a heat pump are slightly cheaper. The average market price for such a unit with a basic set of programs and features is around $450. The best examples in this category are the Electrolux EW6CR527P, Gorenje DP7B, and Candy GVS4H7A1TCEX-S. A similarly functional machine with a heat pump will cost approximately $100 more (around $550 in the Russian market). The following models performed best in this category: Bosch WTW85540EU, Samsung DV90N8287AW, Siemens WT47Y782OE.
More affordable options can be found among both types of dryers, but you will have to deal with either a smaller drum load or fewer options.
Therefore, choosing a tumble dryer is primarily determined by budget, desired functionality, and your living conditions. Both heat pump and condensing units are excellent home assistants that will do their job perfectly.
Interesting:
Readers' comments
Headings
Washing machine repair


For buyers
For users

Dishwasher
















Add a comment